It’s easy to get caught up in all the vape accessory hype. What’s more important, though, is understanding what a ccell is and how it works. If you are just a casual user of vape pens or a product manager selling branded vaporizers, understanding the mechanics of the ccell is a helpful tool to engage in the industry.
If you buy vape pen products and accessories, you’ll understand what to buy. If your job focuses on selling or managing vape product lines, you’ll be able to offer retailers or customers not just a product but an experience. There is nothing better for gaining brand loyalty than a well-educated business model. One of the most common problems people face is wondering why their cartridge doesn’t appear full.
Generally, your ccell cartridge isn’t full because the oil has been absorbed into the ceramic core. However, the reason you may see oil in the container may be due to various technical issues with the quality of your vape line.
Let’s dive into a common problem with poor-quality ccell cartridges. The more information you have, the better you can service your clients. Remember that you will always get customers that have questions. Let us give you the answers.
What is a ccell cartridge?
The ccell cartridge holds the main functionality of the vape pen. When you think of vaping, you think of the juice and the heating element. However, many necessary components go into the making of a vape pen. So let’s chat a little more about how the magic happens.
When you take a hit, you pull vapor out of the cartridge. But how does this all happen?
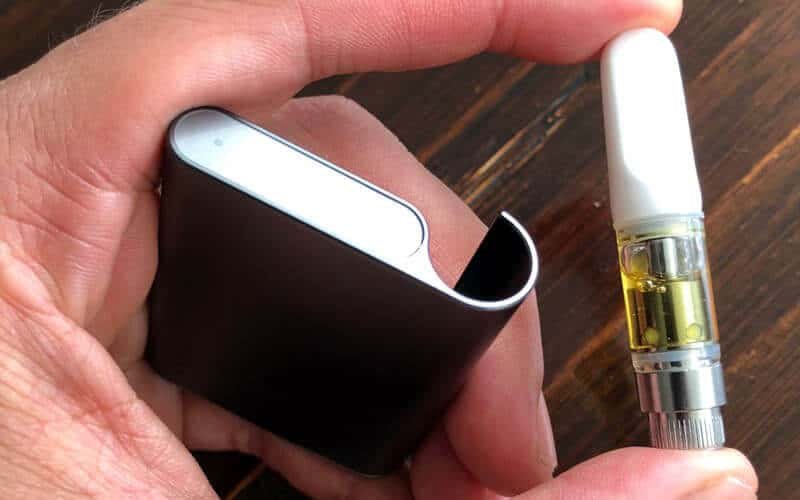
The ccell cartridge contains everything but the battery. If you buy a disposable pen, the battery is probably already attached. However, often you just buy the cartridge and connect a separate 510-threaded vape battery. Here is what happens inside the cartridge.
- First, the vape liquid, juice, or dry bud buddies up to the heating element. Therefore, you might see a spare room if it’s filled with liquid. It soaks into the material.
- Second, the heating element heats up, or atomizes, the liquid to the evaporation point. This is the point at which the fluid is vaporized via evaporation. This is different than boiling. The boiling temperature is above the vapor temperature. Therefore, the cannabis compounds shouldn’t be heated to the boiling point for quality.
- Third, you take a hit and pull vapor, not smoke, into your lungs.
So, when you think ccell cartridge, think about quality, technology, efficiency, and a more consistent cannabis experience.
The structure of a ccell cartridge
Let’s get more technical and specific with the ccell vape pen.
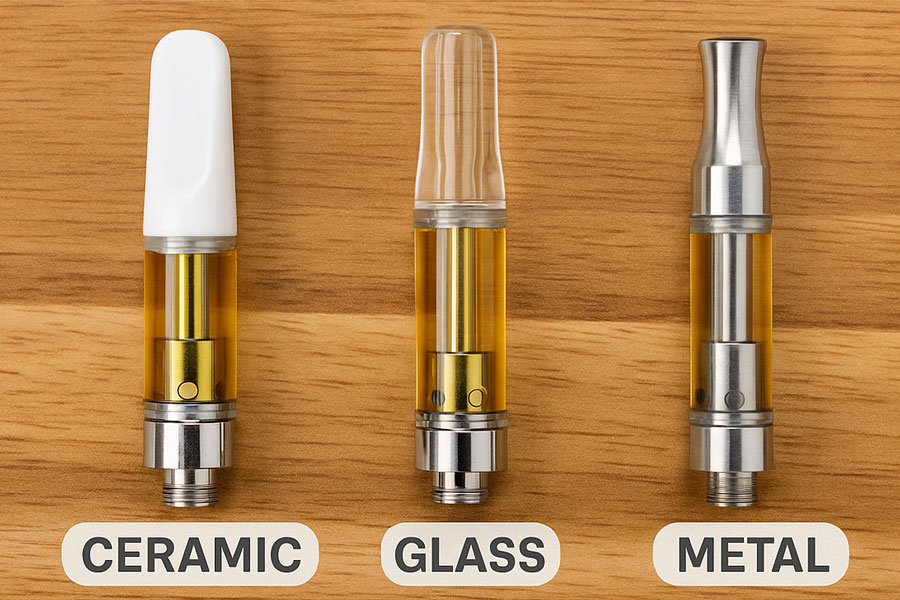
Mouthpiece
The mouthpiece is the topmost part of the ccell vape pen. This part can be made of plastic, metal, or ceramic. Costs will vary based on the material. Further, manufacturing time differs as plastic and ceramic mouthpieces take longer to build. Metal mouthpieces are made quickly via an automatic lathe. Molding fees are required for custom jobs that have unique mouthpieces.
Glass Tube
Next down the pen is the outer shell, a glass tube. The mouthpiece is attached to the glass tube via a silicone ring. This secures the seal and stops any leakage.
Atomizing Tube & Cartridge Base & Pin
The atomizing tube runs the cartridge length from the mouthpiece to the cartridge base. High-quality atomizer tubes are brass, and some are stainless steel for lead-free cartridges. Tubes made of zinc alloy are employed for cheaper cartridges.
The cartridge base connects to the atomizer tube and the outer glass tube. So, the glass tube is sealed at the top by the mouthpiece and at the bottom by the metal cartridge base. The cartridge base usually has two (2) or four (4) holes. These are air holes for when you take a hit.
The bottom of the cartridge base has the electrode pin for the battery connection. This is usually a 510-thread battery slot.
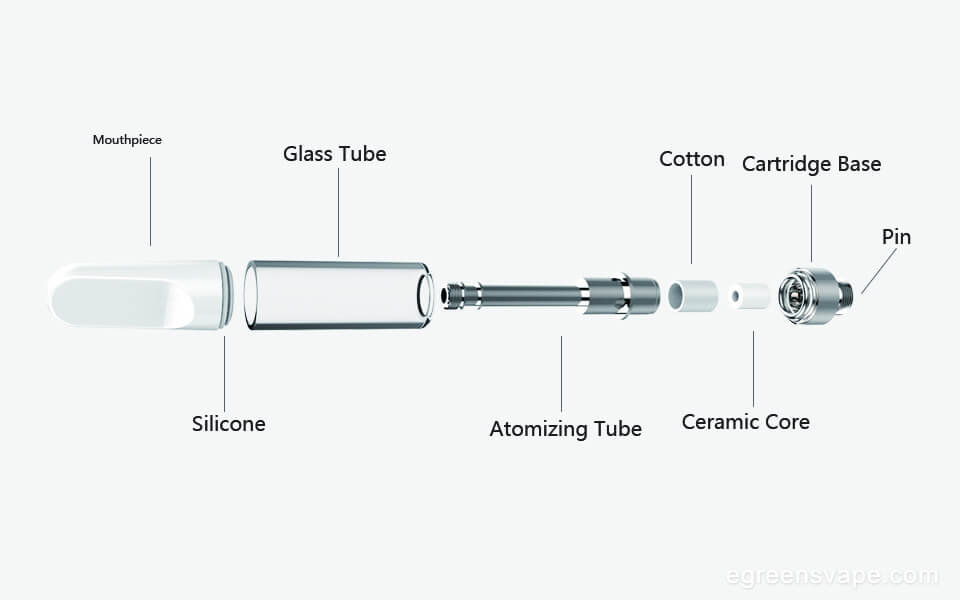
Ceramic Core and Cotton Sheath
A nickel heating coil shrouded in a porous ceramic core makes up the element that converts the liquid to the vapor stage. The ceramic core is housed within a cotton sheath. These ceramic cores are generally circular but can be pad or T-shaped. The cotton and the porous ceramic core soak up the oils.
You can see the cannabis liquid through the glass tube when you look at the cartridge. When the cartridges are filled, they are adequately filled and consistently made. However, as the liquid settles, it soaks into the cotton and starts to permeate the porous ceramic core. This is why you may see air bubbles or extra space in the cartridge.
Battery
Most ccell cartridges use a standard lithium-Ion battery. These are usually placed at the bottom of the cartridge. You can buy cartridges that allow for recharging or single-use. The battery doesn’t just electrify the heating element. Instead, it must send an electrical current through the heating element at the proper current such that the resistance factor in the metals heat the ceramic core to a specific temperature. If it is too cold, nothing will happen. If it is too hot, the liquid will burn.
The structure of the ceramic core
As referenced above, the e-cig is defined as a heating element submerged in a liquid. A battery powers the heating element. The fluid is heated to the evaporation point but not as high as the boiling point. This basic process creates the vapor that is inhaled through the mouthpiece.
However, even older model e-cigs did not include a bare heating element to the liquid. Instead, older models traditionally used a material that could be saturated by the fluid so that the heat would evenly distribute through the liquid. Think of a candle. The flame burns evenly over the candle’s life because the wick is evenly saturated with the candle wax or candle fat.
Technology improvements over the past decade have led to ccell cartridges. Ccell stands for ceramic cell. Ceramic replaces older models that base the saturating material on cotton or cloth. These varieties would inherently burn out or heat non-uniformly. Ceramic cells are like ceramic tiles or ceramic cookware. It is a highly durable material that isn’t damaged by heat, even after prolonged exposure to temperature fluctuations.
So, over the long term, ceramic cell cartridges will last and provide better quality vapor to the end-user. In addition, the internal workings of the ccell allow long-term consistency in taste. Cotton is still used but is used to wrap the ceramic core.
What would you see if you cut the ceramic cell (ccell) in half? The ceramic isn’t a solid piece of hardened material. Instead, it is a high-porous fabricated cell hardened around a heating element. Think of a Slinky or a spring. Now take that spring and put it in a tube filled with cement. When set, you have a spring suspended in a cylinder of cement.
With a ccell, the only difference is that the material is a ceramic material that is porous enough to allow your vape liquid to penetrate through to the heating coil. In addition, the ceramic material heats uniformly, and with more surface area (due to the pores), there is more evaporation at a given temperature.
EGreens’ Ceramic Core Structure
Our ceramic core consists of hundreds of millions of micropores; when heated, it produces vapor. The critical variables for a quality ceramic core are water absorption, porosity, density. The water absorption and porosity of the material will affect the oil absorption. There is a balance between porosity, water absorption, and even cotton density. Too much or too little will lead to poor quality vapor and a less than pleasant experience.
The average pore size of our ceramic cells is equivalent to one-fifth the diameter of human hair. These tiny pores are the key to the ceramic atomizing core to achieve stable liquid guiding and liquid locking functions. Due to surface tension and capillary action, the liquid can penetrate the atomizing core uniformly and be adsorbed on the surface of the atomizing core.

Typical ceramics on the market have a water absorption rate of 30%-60% and a porosity of 40%-55%. We generally choose ceramics with a water absorption rate of 35%-45% and a porosity of 45%-50%. We have tested many ceramics on the market and found a big difference in water absorption.
Using ceramics with higher water absorption allows faster oil absorption and better smoke continuation but may also lead to the risk of oil leakage. Therefore, if the water absorption rate of the ceramic is high, then the oil in the atomization chamber will be absorbed quickly, which is why your atomizer is not full. Oil leakage occurs when the absorbed oil exceeds the adsorption capacity of the ceramic core.
Another cause of dissatisfaction with the atomizer is cotton. As mentioned before, the ceramic core is wrapped in cotton. We use 70-75g cotton, while others use 80g cotton. The looser the cotton wraps, the larger the gap between the cotton, the more oil may be absorbed. On the contrary, the tighter the cotton wraps, the less oil will be absorbed, leading to less smoke.
Bottom Line
Knowledge is power. If you have questions regarding your ccell cartridges or just want to know more about the manufacturing process, reach out to us, and we will be happy to help answer your questions.











